With an area of 5 million hectares, India produces sugarcane on about 2.57 % of the total cropped area. It employs around 60 lakh sugarcane growers and indirectly employs many people in the association. (as of Feb 2022)
Sugarcane is a tropical as well as a subtropical crop. It grows well in hot and humid climates with a temperature of 21°C−27°C and annual rainfall between 75 cm and 100 cm. Well-drained loamy soil with pH 6.5 – 7.5 and adequate nutrients without soil compaction is considered an ideal soil for its production.
An average crop of sugarcane yielding 100 t/ha removes 208kg of N, 53kg of P, 280kg of K, 30 kg of Sulphur, 3.4kg of iron, and 1.2 kg of manganese, 0.6 kg of copper, respectively, from the soil. Thus, the soil must be kept healthy & fertile for a better yield.

However, infections & diseases can all occur if the crops aren’t taken care of. Most conditions seem beyond the farmer’s control, but a few tips can prevent or overcome them. Some of the significant sugarcane diseases are mentioned below with their control measures.
Eye spot: Small water-soaked spots on leaves; elongated water-soaked spots in the shape of an eye; straw-colored lesions with a reddish-brown center develop from water-soaked lesions.
Control measure:
- The application of appropriate foliar fungicides can control this disease.
Pineapple disease: Setts not rooting; the soft central portion of set has red discoloration which turns brown-black; cavities in infected internodes; In older canes, leaves may be yellowing, and the plant appears withered; the cut stem has a strong smell of pineapple
Control measure:
- The most effective method of managing the disease is through the use of resistant sugarcane varieties; if planting varieties that are susceptible to the disease, then grow them in dry, well-draining soils
Red rot: Yellowing, drying leaves; elongated red lesions on leaf midribs which may develop a yellow straw center; splitting open the stalk lengthwise reveals reddish patches of tissue interrupted by white areas; vascular tissue may also be red
Control measure:
- Planting resistant sugarcane varieties are the most effective method of controlling this disease.
- Remove crop debris from the plantation to reduce inoculum levels; rogue diseased plants.
- Treating seed pieces with hot water before planting can reduce the incidence of the disease, but foliar fungicide application has proved to be an ineffective method of control.
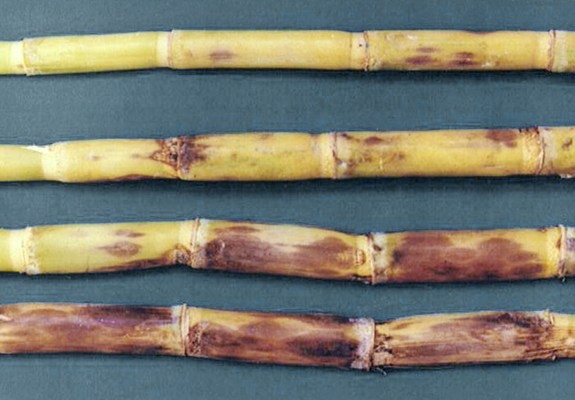
Sugarcane smut disease: Stunted growth of sugarcane stools; profuse production of tillers; shortened internodes; stems thinly with narrow, erect leaves; black whip-like structure emerging from the terminal bud
Control measure:
- Plant varieties of sugarcane that are resistant to the disease.
- Treat the seeds with hot water before planting.
- Remove damaged or infected plants.
Leaf scald: White “pencil line” extending the entire length of leaf lamina; etiolated leaves; leaf tips drying out, resulting in a scalded appearance
Control measure:
- Plant-resistant sugarcane varieties are the most effective method of preventing the disease.
- Treatment of seed cane with hot water to clean the material before planting can help to prevent the disease.
Mosaic: Distinct patterns on contrasting greens on leaves, i.e., dark green patches surrounded by paler green; reddening of leaves; leaf necrosis
Control measure:
- Plant varieties of sugarcane that are tolerant of viruses

Conclusion
Sugarcane (sugar) will likely gain better prices in the upcoming festive season. However, the Indian government has hiked sugarcane FRP (Fair and Remunerative Price) from Rs 15/quintal to Rs 305/-quintal for the 2022-23 season. Hence it’ll be a good choice for farmers to produce sugarcanes as this rise in FRP will benefit around five crore farmers across the country.








 Connect With Us
Connect With Us